Postfix is a great program that routes and delivers email to accounts that are external to the system. It is currently used by approximately 33% of internet mail servers. In this article, I'll explain how you can use Postfix to send mail using Gmail with two-factor authentication enabled.
Before you get Postfix up and running, however, you need to have some items lined up. Following are instructions on how to get it working on a number of distros.
Prerequisites
- An installed OS (Ubuntu/Debian/Fedora/Centos/Arch/FreeBSD/OpenSUSE)
- A Google account with two-factor authentication
- A working internet connection
Step 1: Prepare Google
Open a web browser and log into your Google account. Once you’re in, go to your settings by clicking your picture and selecting "Google Account.” Click “Sign-in & security” and scroll down to "App passwords.” Use your password to log in. Then you can create a new app password (I named mine "postfix Setup”).
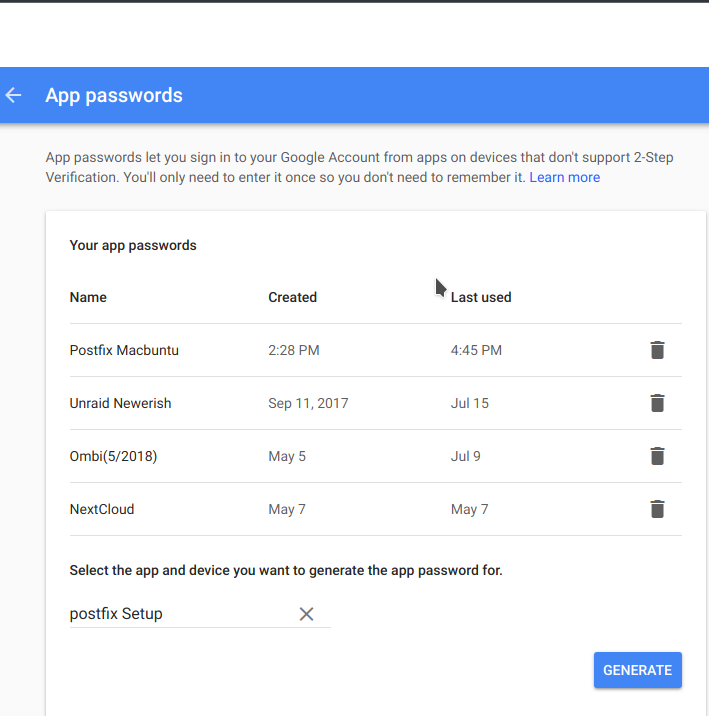
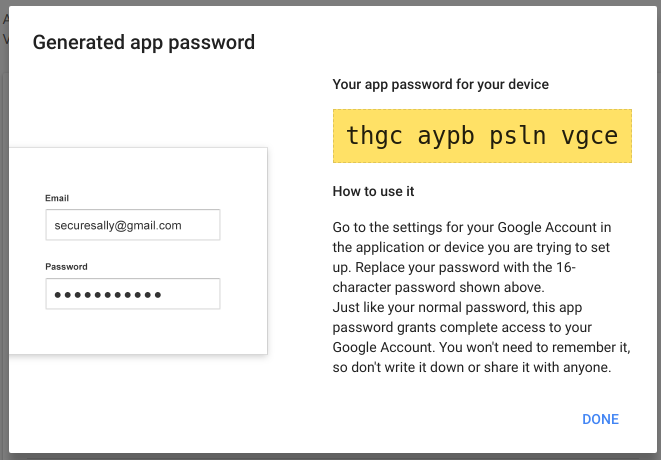
Note the crazy password (shown below), which I will use throughout this article.
Step 2: Install Postfix
Before you can configure the mail client, you need to install it. You must also install either the mailutils or mailx utility, depending on the OS you're using. Here's how to install it for each OS:
Debian/Ubuntu:
apt-get update && apt-get install postfix mailutilsFedora:
dnf update && dnf install postfix mailxCentos:
yum update && yum install postfix mailx cyrus-sasl cyrus-sasl-plainArch:
pacman -Sy postfix mailutilsFreeBSD:
portsnap fetch extract update
cd /usr/ports/mail/postfix
make configIn the configuration dialog, select "SASL support." All other options can remain the same.
From there: make install clean
Install mailx from the binary package: pkg install mailx
OpenSUSE:
zypper update && zypper install postfix mailx cyrus-saslStep 3: Set up Gmail authentication
Once you've installed Postfix, you can set up Gmail authentication. Since you have created the app password, you need to put it in a configuration file and lock it down so no one else can see it. Fortunately, this is simple to do:
Ubuntu/Debian/Fedora/Centos/Arch/OpenSUSE:
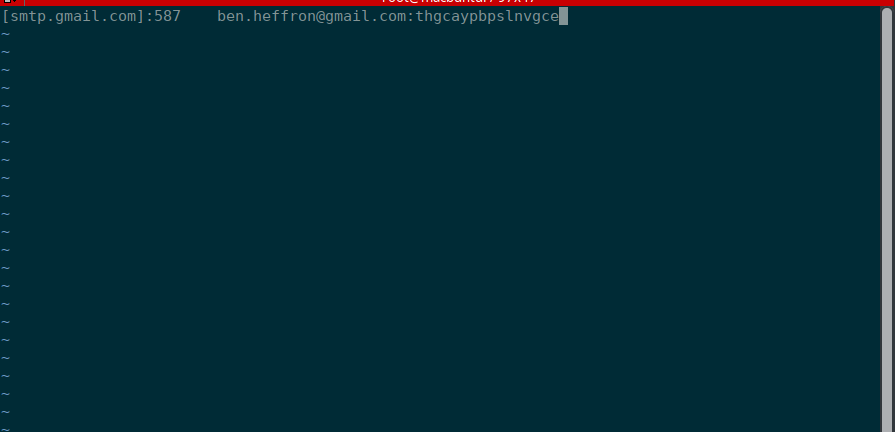
vim /etc/postfix/sasl_passwdAdd this line:
[smtp.gmail.com]:587 ben.heffron@gmail.com:thgcaypbpslnvgceSave and close the file. Since your Gmail password is stored as plaintext, make the file accessible only by root to be extra safe.
chmod 600 /etc/postfix/sasl_passwdFreeBSD:
vim /usr/local/etc/postfix/sasl_passwdAdd this line:
[smtp.gmail.com]:587 ben.heffron@gmail.com:thgcaypbpslnvgceSave and close the file. Since your Gmail password is stored as plaintext, make the file accessible only by root to be extra safe.
chmod 600 /usr/local/etc/postfix/sasl_passwd
Step 4: Get Postfix moving
This step is the "meat and potatoes"—everything you've done so far has been preparation.
Postfix gets its configuration from the main.cf file, so the settings in this file are critical. For Google, it is mandatory to enable the correct SSL settings.
Here are the six options you need to enter or update on the main.cf to make it work with Gmail (from the SASL readme):
- The smtp_sasl_auth_enable setting enables client-side authentication. We will configure the client’s username and password information in the second part of the example.
- The relayhost setting forces the Postfix SMTP to send all remote messages to the specified mail server instead of trying to deliver them directly to their destination.
- With the smtp_sasl_password_maps parameter, we configure the Postfix SMTP client to send username and password information to the mail gateway server.
- Postfix SMTP client SASL security options are set using smtp_sasl_security_options, with a whole lot of options. In this case, it will be nothing; otherwise, Gmail won’t play nicely with Postfix.
- The smtp_tls_CAfile is a file containing CA certificates of root CAs trusted to sign either remote SMTP server certificates or intermediate CA certificates.
- From the configure settings page: stmp_use_tls uses TLS when a remote SMTP server announces STARTTLS support, the default is not using TLS.
Ubuntu/Debian/Arch
These three OSes keep their files (certificates and main.cf) in the same location, so this is all you need to put in there:
vim /etc/postfix/main.cfIf the following values aren’t there, add them:
relayhost = [smtp.gmail.com]:587
smtp_use_tls = yes
smtp_sasl_auth_enable = yes
smtp_sasl_security_options =
smtp_sasl_password_maps = hash:/etc/postfix/sasl_passwd
smtp_tls_CAfile = /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crtSave and close the file.
Fedora/CentOS
These two OSes are based on the same underpinnings, so they share the same updates.
vim /etc/postfix/main.cfIf the following values aren’t there, add them:
relayhost = [smtp.gmail.com]:587
smtp_use_tls = yes
smtp_sasl_auth_enable = yes
smtp_sasl_security_options =
smtp_sasl_password_maps = hash:/etc/postfix/sasl_passwd
smtp_tls_CAfile = /etc/ssl/certs/ca-bundle.crtSave and close the file.
OpenSUSE
vim /etc/postfix/main.cfIf the following values aren’t there, add them:
relayhost = [smtp.gmail.com]:587
smtp_use_tls = yes
smtp_sasl_auth_enable = yes
smtp_sasl_security_options =
smtp_sasl_password_maps = hash:/etc/postfix/sasl_passwd
smtp_tls_CAfile = /etc/ssl/ca-bundle.pemSave and close the file.
OpenSUSE also requires that you modify the Postfix master process configuration file master.cf. Open it for editing:
vim /etc/postfix/master.cfUncomment the line that reads:
#tlsmgr unix - - n 1000? 1 tlsmgIt should look like this:
tlsmgr unix - - n 1000? 1 tlsmgSave and close the file.
FreeBSD
vim /usr/local/etc/postfix/main.cfIf the following values aren’t there, add them:
relayhost = [smtp.gmail.com]:587
smtp_use_tls = yes
smtp_sasl_auth_enable = yes
smtp_sasl_security_options =
smtp_sasl_password_maps = hash:/usr/local/etc/postfix/sasl_passwd
smtp_tls_CAfile = /etc/mail/certs/cacert.pemSave and close the file.
Step 5: Set up the password file
Remember that password file you created? Now you need to feed it into Postfix using postmap. This is part of the mailutils or mailx utilities.
Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora, CentOS, OpenSUSE, Arch Linux
postmap /etc/postfix/sasl_passwdFreeBSD
postmap /usr/local/etc/postfix/sasl_passwd Step 6: Get Postfix grooving
To get all the settings and configurations working, you must restart Postfix.
Debian, Ubuntu, Fedora, CentOS, OpenSUSE, Arch Linux
These guys make it simple to restart:
systemctl restart postfix.serviceFreeBSD
To start Postfix at startup, edit /etc/rc.conf:
vim /etc/rc.confAdd the line:
postfix_enable=YESSave and close the file. Then start Postfix by running:
service postfix startStep 7: Test it
Now for the big finale—time to test it to see if it works. The mail command is another tool installed with mailutils or mailx.
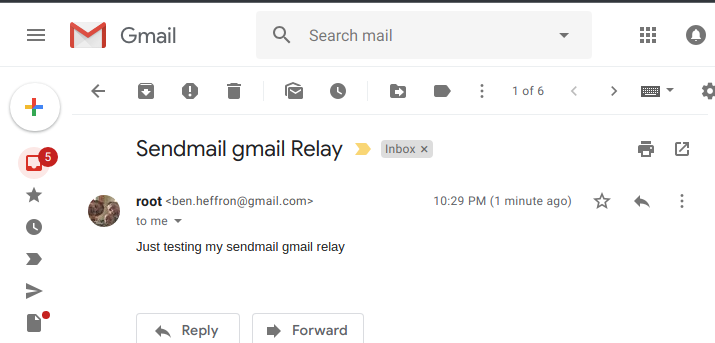
echo Just testing my sendmail gmail relay" | mail -s "Sendmail gmail Relay" ben.heffron@gmail.comThis is what I used to test my settings, and then it came up in my Gmail.
Now you can use Gmail with two-factor authentication in your Postfix setup.






Comments are closed.