Moving files in Linux can seem relatively straightforward, but there are more options available than most realize. This article teaches beginners how to move files in the GUI and on the command line, but also explains what’s actually happening under the hood, and addresses command line options that many experience users have rarely explored.
Moving what?
Before delving into moving files, it’s worth taking a closer look at what actually happens when moving file system objects. When a file is created, it is assigned to an inode, which is a fixed point in a file system that’s used for data storage. You can find what inode maps to a file with the ls command:
$ ls --inode example.txt
7344977 example.txt
When you move a file, you don’t actually move the data from one inode to another, you only assign the file object a new name or file path. In fact, a file retains its permissions when it’s moved, because moving a file doesn’t change or re-create it.
File and directory inodes never imply inheritance and are dictated by the filesystem itself. Inode assignment is sequential based on when the file was created and is entirely independent of how you organize your computer. A file "inside" a directory may have a lower inode number than its parent directory, or a higher one. For example:
$ mkdir foo
$ mv example.txt foo
$ ls --inode
7476865 foo
$ ls --inode foo
7344977 example.txt
When moving a file from one hard drive to another, however, the inode is very likely to change. This happens because the new data has to be written onto a new filesystem. For this reason, in Linux the act of moving and renaming files is literally the same action. Whether you move a file to another directory or to the same directory with a new name, both actions are performed by the same underlying program.
This article focuses on moving files from one directory to another.
Moving with a mouse
The GUI is a friendly and, to most people, familiar layer of abstraction on top of a complex collection of binary data. It’s also the first and most intuitive way to move files on Linux. If you’re used to the desktop experience, in a generic sense, then you probably already know how to move files around your hard drive. In the GNOME desktop, for instance, the default action when dragging and dropping a file from one window to another is to move the file rather than to copy it, so it’s probably one of the most intuitive actions on the desktop:
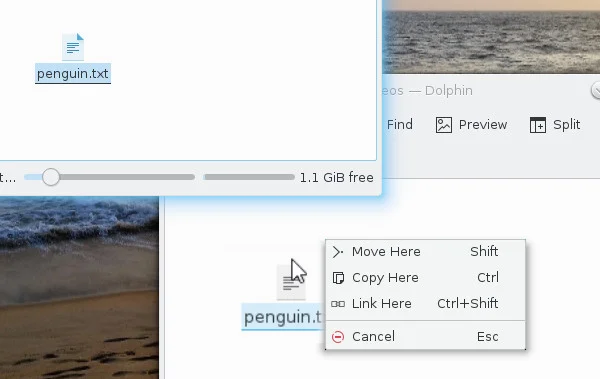
The Dolphin file manager in the KDE Plasma desktop defaults to prompting the user for an action. Holding the Shift key while dragging a file forces a move action:
Moving on the command line
The shell command intended for moving files on Linux, BSD, Illumos, Solaris, and MacOS is mv. A simple command with a predictable syntax, mv <source> <destination> moves a source file to the specified destination, each defined by either an absolute or relative file path. As mentioned before, mv is such a common command for POSIX users that many of its additional modifiers are generally unknown, so this article brings a few useful modifiers to your attention whether you are new or experienced.
Not all mv commands were written by the same people, though, so you may have GNU mv, BSD mv, or Sun mv, depending on your operating system. Command options differ from implementation to implementation (BSD mv has no long options at all) so refer to your mv man page to see what’s supported, or install your preferred version instead (that’s the luxury of open source).
Moving a file
To move a file from one folder to another with mv, remember the syntax mv <source> <destination>. For instance, to move the file example.txt into your Documents directory:
$ touch example.txt
$ mv example.txt ~/Documents
$ ls ~/Documents
example.txt
Just like when you move a file by dragging and dropping it onto a folder icon, this command doesn’t replace Documents with example.txt. Instead, mv detects that Documents is a folder, and places the example.txt file into it.
You can also, conveniently, rename the file as you move it:
$ touch example.txt
$ mv example.txt ~/Documents/foo.txt
$ ls ~/Documents
foo.txt
That’s important because it enables you to rename a file even when you don’t want to move it to another location, like so:
$ touch example.txt
$ mv example.txt foo2.txt
$ ls
foo2.txt
Moving a directory
The mv command doesn’t differentiate a file from a directory the way cp does. You can move a directory or a file with the same syntax:
$ touch file.txt
$ mkdir foo_directory
$ mv file.txt foo_directory
$ mv foo_directory ~/Documents
Moving a file safely
If you copy a file to a directory where a file of the same name already exists, the mv command replaces the destination file with the one you are moving, by default. This behavior is called clobbering, and sometimes it’s exactly what you intend. Other times, it is not.
Some distributions alias (or you might write your own) mv to mv --interactive, which prompts you for confirmation. Some do not. Either way, you can use the --interactive or -i option to ensure that mv asks for confirmation in the event that two files of the same name are in conflict:
$ mv --interactive example.txt ~/Documents
mv: overwrite '~/Documents/example.txt'?
If you do not want to manually intervene, use --no-clobber or -n instead. This flag silently rejects the move action in the event of conflict. In this example, a file named example.txt already exists in ~/Documents, so it doesn't get moved from the current directory as instructed:
$ mv --no-clobber example.txt ~/Documents
$ ls
example.txt
Moving with backups
If you’re using GNU mv, there are backup options offering another means of safe moving. To create a backup of any conflicting destination file, use the -b option:
$ mv -b example.txt ~/Documents
$ ls ~/Documents
example.txt example.txt~
This flag ensures that mv completes the move action, but also protects any pre-existing file in the destination location.
Another GNU backup option is --backup, which takes an argument defining how the backup file is named:
- existing: If numbered backups already exist in the destination, then a numbered backup is created. Otherwise, the simple scheme is used.
- none: Does not create a backup even if --backup is set. This option is useful to override a mv alias that sets the backup option.
- numbered: Appends the destination file with a number.
- simple: Appends the destination file with a ~, which can conveniently be hidden from your daily view with the --ignore-backups option for ls.
For example:
$ mv --backup=numbered example.txt ~/Documents
$ ls ~/Documents
-rw-rw-r--. 1 seth users 128 Aug 1 17:23 example.txt
-rw-rw-r--. 1 seth users 128 Aug 1 17:20 example.txt.~1~
A default backup scheme can be set with the environment variable VERSION_CONTROL. You can set environment variables in your ~/.bashrc file or dynamically before your command:
$ VERSION_CONTROL=numbered mv --backup example.txt ~/Documents
$ ls ~/Documents
-rw-rw-r--. 1 seth users 128 Aug 1 17:23 example.txt
-rw-rw-r--. 1 seth users 128 Aug 1 17:20 example.txt.~1~
-rw-rw-r--. 1 seth users 128 Aug 1 17:22 example.txt.~2~
The --backup option still respects the --interactive or -i option, so it still prompts you to overwrite the destination file, even though it creates a backup before doing so:
$ mv --backup=numbered example.txt ~/Documents
mv: overwrite '~/Documents/example.txt'? y
$ ls ~/Documents
-rw-rw-r--. 1 seth users 128 Aug 1 17:24 example.txt
-rw-rw-r--. 1 seth users 128 Aug 1 17:20 example.txt.~1~
-rw-rw-r--. 1 seth users 128 Aug 1 17:22 example.txt.~2~
-rw-rw-r--. 1 seth users 128 Aug 1 17:23 example.txt.~3~
You can override -i with the --force or -f option.
$ mv --backup=numbered --force example.txt ~/Documents
$ ls ~/Documents
-rw-rw-r--. 1 seth users 128 Aug 1 17:26 example.txt
-rw-rw-r--. 1 seth users 128 Aug 1 17:20 example.txt.~1~
-rw-rw-r--. 1 seth users 128 Aug 1 17:22 example.txt.~2~
-rw-rw-r--. 1 seth users 128 Aug 1 17:24 example.txt.~3~
-rw-rw-r--. 1 seth users 128 Aug 1 17:25 example.txt.~4~
The --backup option is not available in BSD mv.
Moving many files at once
When moving multiple files, mv treats the final directory named as the destination:
$ mv foo bar baz ~/Documents
$ ls ~/Documents
foo bar baz
If the final item is not a directory, mv returns an error:
$ mv foo bar baz
mv: target 'baz' is not a directory
The syntax of GNU mv is fairly flexible. If you are unable to provide the mv command with the destination as the final argument, use the --target-directory or -t option:
$ mv --target-directory=~/Documents foo bar baz
$ ls ~/Documents
foo bar baz
This is especially useful when constructing mv commands from the output of some other command, such as the find command, xargs, or GNU Parallel.
Moving based on mtime
With GNU mv, you can define a move action based on whether the file being moved is newer than the destination file it would replace. This option is possible with the --update or -u option, and is not available in BSD mv:
$ ls -l ~/Documents
-rw-rw-r--. 1 seth users 128 Aug 1 17:32 example.txt
$ ls -l
-rw-rw-r--. 1 seth users 128 Aug 1 17:42 example.txt
$ mv --update example.txt ~/Documents
$ ls -l ~/Documents
-rw-rw-r--. 1 seth users 128 Aug 1 17:42 example.txt
$ ls -l
This result is exclusively based on the files’ modification time, not on a diff of the two files, so use it with care. It’s easy to fool mv with a mere touch command:
$ cat example.txt
one
$ cat ~/Documents/example.txt
one
two
$ touch example.txt
$ mv --update example.txt ~/Documents
$ cat ~/Documents/example.txt
one
Obviously, this isn’t the most intelligent update function available, but it offers basic protection against overwriting recent data.
Moving
There are more ways to move data than just the mv command, but as the default program for the job, mv is a good universal option. Now that you know what options you have available, you can use mv smarter than ever before.







1 Comment