Network routing protocols fall into two main categories: interior gateway protocols and exterior gateway protocols. Interior gateway protocols are used by routers to share information within a single autonomous system. If you are running Linux, you can make your system behave as a router through the open source (GPLv2) routing stack Quagga.
What is Quagga?
Quagga is a routing software suite and a fork of GNU Zebra. It provides implementations of all major routing protocols such as Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), Routing Information Protocol (RIP), Border Gateway Protocol (BGP), and Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS) for Unix-like platforms.
Although Quagga implements the routing protocols for both IPv4 and IPv6, it doesn't act as a complete router. A true router not only implements all the routing protocols but also has the ability to forward network traffic. Quagga only implements the routing stack, and the job of forwarding network traffic is handled by the Linux kernel.
Architecture
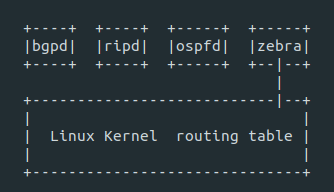
Quagga implements the different routing protocols through protocol-specific daemons. The daemon name is the same as the routing protocol followed by the letter "d." Zebra is the core and a protocol-independent daemon that provides an abstraction layer to the kernel and presents the Zserv API over TCP sockets to Quagga clients. Each protocol-specific daemon is responsible for running the relevant protocol and building the routing table based on the information exchanged.
Setup
This tutorial implements the OSPF protocol to configure dynamic routing using Quagga. The setup includes two CentOS 7.7 hosts, named Alpha and Beta. Both hosts share access to the 192.168.122.0/24 network.
Host Alpha:
IP: 192.168.122.100/24
Gateway: 192.168.122.1
Host Beta:
IP: 192.168.122.50/24
Gateway: 192.168.122.1
Install the package
First, install the Quagga package on both hosts. It is available in the CentOS base repo:
yum install quagga -yEnable IP forwarding
Next, enable IP forwarding on both hosts since that will performed by the Linux kernel:
sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
sysctl -pConfiguration
Now, go into the /etc/quagga directory and create the configuration files for your setup. You need three files:
- zebra.conf: Quagga's daemon configuration file, which is where you'll define the interfaces and their IP addresses and IP forwarding
- ospfd.conf: The protocol configuration file, which is where you'll define the networks that will be offered through the OSPF protocol
- daemons: Where you'll specify the relevant protocol daemons that are required to run
On host Alpha,
[root@alpha]# cat /etc/quagga/zebra.conf
interface eth0
ip address 192.168.122.100/24
ipv6 nd suppress-ra
interface eth1
ip address 10.12.13.1/24
ipv6 nd suppress-ra
interface lo
ip forwarding
line vty
[root@alpha]# cat /etc/quagga/ospfd.conf
interface eth0
interface eth1
interface lo
router ospf
network 192.168.122.0/24 area 0.0.0.0
network 10.12.13.0/24 area 0.0.0.0
line vty
[root@alphaa ~]# cat /etc/quagga/daemons
zebra=yes
ospfd=yesOn host Beta,
[root@beta quagga]# cat zebra.conf
interface eth0
ip address 192.168.122.50/24
ipv6 nd suppress-ra
interface eth1
ip address 10.10.10.1/24
ipv6 nd suppress-ra
interface lo
ip forwarding
line vty
[root@beta quagga]# cat ospfd.conf
interface eth0
interface eth1
interface lo
router ospf
network 192.168.122.0/24 area 0.0.0.0
network 10.10.10.0/24 area 0.0.0.0
line vty
[root@beta ~]# cat /etc/quagga/daemons
zebra=yes
ospfd=yesConfigure the firewall
To use the OSPF protocol, you must allow it in the firewall:
firewall-cmd --add-protocol=ospf –permanent
firewall-cmd –reloadNow, start the zebra and ospfd daemons.
# systemctl start zebra
# systemctl start ospfdLook at the route table on both hosts using:
[root@alpha ~]# ip route show
default via 192.168.122.1 dev eth0 proto static metric 100
10.10.10.0/24 via 192.168.122.50 dev eth0 proto zebra metric 20
10.12.13.0/24 dev eth1 proto kernel scope link src 10.12.13.1
192.168.122.0/24 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.122.100 metric 100You can see that the routing table on Alpha contains an entry of 10.10.10.0/24 via 192.168.122.50 offered through protocol zebra. Similarly, on host Beta, the table contains an entry of network 10.12.13.0/24 via 192.168.122.100.
[root@beta ~]# ip route show
default via 192.168.122.1 dev eth0 proto static metric 100
10.10.10.0/24 dev eth1 proto kernel scope link src 10.10.10.1
10.12.13.0/24 via 192.168.122.100 dev eth0 proto zebra metric 20
192.168.122.0/24 dev eth0 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.122.50 metric 100Conclusion
As you can see, the setup and configuration are relatively simple. To add complexity, you can add more network interfaces to the router to provide routing for more networks. You can also implement BGP and RIP protocols using the same method.








5 Comments