Flutter is the newest addition to Google's programming cadre. Following the success of Android, Kotlin, and Golang, Flutter was created as a cross-platform application development language. It is primarily based on the Dart programming construct and is considered to be the next big programming paradigm because its code can run as a mobile app, a web app, and even a desktop app without any major changes. Supposedly it will support Google's upcoming Fuschia operating system.
Flutter plugins are simple dependencies that extend the language's capabilities. This list of the top five open source Flutter plugins includes both user interface (UI)-related and function-related plugins.
The plugins must be included in your pubspec.yaml file before they can be used; they are required to make modifications to the pubspec.yaml file in the lib folder inside the project.
Flutter video-player plugin
The video_player plugin allows you to embed videos to play in Flutter apps.
Note: Up to Flutter 1.9, there is no video player support present in Flutter, so you have to depend on external plugins like video_player. This provides us with the VideoPlayer class which we will be using here.
Before using the VideoPlayer class in Flutter, you have to do the following for iOS and Android applications.
Prerequisites
For Android:
Make sure that the minimum SDK is set to 21. You can modify this through the Build Gradle inside the android>app folder.
Next, make sure that the AndroidManifest.xml file has internet permission enabled by adding the following line in the AndroidManifest.xml file:
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>For iOS:
To give permission to use the internet to render the videos (if required), add the following lines to the info.plist file in <project root>/ios/Runner/Info.plist:
<key>NSAppTransportSecurity</key>
<dict>
<key>NSAllowsArbitraryLoads</key>
<true/>
</dict>Once the prerequisites for Android and iOS are done, add the following line to the pubspec.yaml file in the dependency section:
dependencies: video_player: ^0.10.1+3Then use get packages to sync the project.
Video_Player plugin basics
The Video_Player plugin provides support for playing network and local videos on a device by creating a simple API to call the videos. The example application below shows how the Video_Player plugin uses the controller object and how to create the Future<> Builder to play the video on loading.
Start by using the Scaffold widget as the parent body widget. The goal is for the user to be able to play and pause a video using button controls.
In order to call the video player object from anywhere, you need a controller to hold it. The VideoPlayerController class makes this possible. The example application pieces it all together.
Example Flutter Video Player app
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:video_player/video_player.dart';
void main() => runApp(VideoPlayerApp());
class VideoPlayerApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Video Player Demo',
home: VideoPlayerScreen(),
);
}
}
class VideoPlayerScreen extends StatefulWidget {
VideoPlayerScreen({Key key}) : super(key: key);
@override
_VideoPlayerScreenState createState() => _VideoPlayerScreenState();
}
class _VideoPlayerScreenState extends State<VideoPlayerScreen> {
VideoPlayerController _controller;
Future<void> _initializeVideoPlayerFuture;
@override
void initState() {
_controller = VideoPlayerController.network(
'https://flutter.github.io/assets-for-api-docs/assets/videos/bee.mp4',
);
// Initialize the controller and store the Future for later use.
_initializeVideoPlayerFuture = _controller.initialize();
// Use the controller to loop the video.
_controller.setLooping(true);
super.initState();
}
@override
void dispose() {
// Ensure disposing of the VideoPlayerController to free up resources.
_controller.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
drawer: Drawer(),
backgroundColor: Colors.orangeAccent,
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Bee Video'),
backgroundColor: Colors.black87,
),
// Use a FutureBuilder to display a loading spinner while waiting for the
// VideoPlayerController to finish initializing.
body: Stack(
children: <Widget>[
Center(child:FutureBuilder(
future: _initializeVideoPlayerFuture,
builder: (context, snapshot) {
if (snapshot.connectionState == ConnectionState.done) {
// If the VideoPlayerController has finished initialization, use
// the data it provides to limit the aspect ratio of the video.
return AspectRatio(
aspectRatio: _controller.value.aspectRatio,
// Use the VideoPlayer widget to display the video.
child: VideoPlayer(_controller),
);
} else {
// If the VideoPlayerController is still initializing, show a
// loading spinner.
return Center(child: CircularProgressIndicator());
}
},
)),
Center(
child:
ButtonTheme(
height: 100.0,
minWidth: 200.0,
child: RaisedButton(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(60.0),
color: Colors.transparent,
textColor: Colors.white,
onPressed: () {
// Wrap the play or pause in a call to `setState`. This ensures the
// correct icon is shown.
setState(() {
// If the video is playing, pause it.
if (_controller.value.isPlaying) {
_controller.pause();
} else {
// If the video is paused, play it.
_controller.play();
}
});
},
child: Icon(
_controller.value.isPlaying ? Icons.pause : Icons.play_arrow,
size: 120.0,
),
))
)
],
),
);
}
}Here's the resulting application.


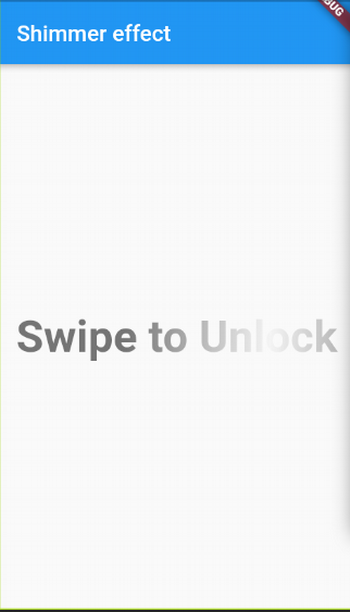
Flutter Shimmer Effect plugin
The Flutter Shimmer Effect UI plugin is fairly straightforward: You just make use of only one class in your widget tree, and the work is done. Here is what the Shimmer Effect looks like:

To implement this effect, jump into the widget definition and use the Shimmer class in your widget tree with this option:
Shimmer.fromColorsNext, finalize the application by filling out the properties described below.
Shimmer.fromColors properties
Shimmer.fromColors has the following properties:
- baseColor: This is the shimmer's base color that gets shown on the widget. This is the primary color and the one the child widget will use.
- HighlightColor: This is the color that produces the shimmer-like effect by continually waving across the child widget.
- Child: This holds whatever widget produces the Shimmer Effect. It could be a Text widget or any complex structure.
The example program shows how these attributes work across complex widgets.
Example Flutter Shimmer Effect app
This example produces the Shimmer Effect for two important widgets: the Text widget and the Listview widget.
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:shimmer/shimmer.dart';
void main() => runApp(ShimmerEffectApp());
class ShimmerEffectApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Sample ShimmerEffect Widget',
home: ShimmerWidget(),
);
}
}
class ShimmerWidget extends StatefulWidget {
ShimmerWidget({Key key}) : super(key: key);
@override
_ShimmerWidgetState createState() => _ShimmerWidgetState();
}
class _ShimmerWidgetState extends State {
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("Shimmer effect"),),
body: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(25.0),
child:Center(
child: Shimmer.fromColors(
direction: ShimmerDirection.rtl,
period: Duration(seconds:5),
child: Column(
children: [0, 1, 2, 3]
.map((_) => Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.only(bottom: 8.0),
child: Row(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
Container(
width: 48.0,
height: 48.0,
color: Colors.white,
),
Padding(
padding:
const EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 8.0),
),
Expanded(
child: Column(
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: [
Container(
width: double.infinity,
height: 8.0,
color: Colors.white,
),
Padding(
padding:
const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 2.0),
),
Container(
width: double.infinity,
height: 8.0,
color: Colors.white,
),
Padding(
padding:
const EdgeInsets.symmetric(vertical: 2.0),
),
Container(
width: 40.0,
height: 8.0,
color: Colors.white,
),
],
),
)
],
),
))
.toList(),
),
baseColor: Colors.grey[700],
highlightColor: Colors.grey[100]),
)
),
);
}
}Here's the resulting application.

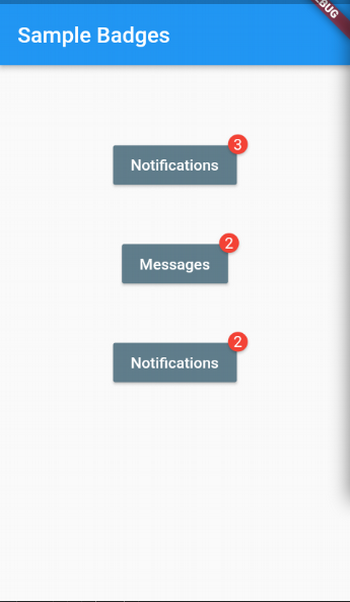
Flutter Badges plugin
Flutter Badges is a very useful UI plugin that marks a notification count, a count of items in an e-commerce basket, etc.
To use the Flutter Badges plugin, add the following dependency in your pubspec.yaml file:
dependencies:
badges: ^1.1.0Then, import the following line into your main.dart file:
import 'package:badges/badges.dart';Now, you can create badges with a simple call to the Badge class.
Badge class properties
Following are the Badge class's available properties:
- badgeContent: This is the attribute that takes in the value of the Badge. It could be a number, a letter, etc. Make sure to make it as small as possible!
- BadgeColor: Control the color of the badge by adjusting the BadgeColor colors property.
- AnimationType: This enables three animations for the Badge:
- BadgeAnimationType.scale: Scales animation once loading happens.
- BadgeAnimationType.fade: Fades animation once loading happens
- BadgeAnimationType.slide: Slides animation once loading happens
- shape: This controls the shape of the badge; it could be a circle or a square.
- AnimationDuration: This takes in a Duration class as its value to set how long the animation should last.
Once these attributes are set, you can create a simple app like the following.
Example Flutter Badge application
Add the following to your main.dart file and run the application.
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:badges/badges.dart';
void main() => runApp(BadgesApp());
class BadgesApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return new MaterialApp(
title: 'APP',
home: BadgesWidget(),
);
}
}
class BadgesWidget extends StatefulWidget {
BadgesWidget({Key key}) : super(key: key);
@override
_BadgesWidgetState createState() => _BadgesWidgetState();
}
class _BadgesWidgetState extends State {
int value = 0;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title:Text("Sample Badges")),
body: Center(
child: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(25.0),
child: Column(
children: [
Spacer(),
Badge(
child: RaisedButton(
color: Colors.blueGrey,
child: Text("Notifications", style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),),
onPressed: (){
setState(() {
value = value + 1;
});
},),
badgeContent: Text('$value',style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),),
badgeColor: Colors.red,
animationType: BadgeAnimationType.scale,
animationDuration: Duration(milliseconds: 500),
shape: BadgeShape.circle,
),
Spacer(),
Badge(
child: RaisedButton(
color: Colors.blueGrey,
child: Text("Messages", style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),),
onPressed: (){
},),
badgeContent: Text("2",style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),),
badgeColor: Colors.red,
animationType: BadgeAnimationType.scale,
animationDuration: Duration(seconds: 1),
shape: BadgeShape.circle,
),
Spacer(),
Badge(
child: RaisedButton(
color: Colors.blueGrey,
child: Text("Notifications", style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),),
onPressed: (){
},),
badgeContent: Text("2",style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),),
badgeColor: Colors.red,
animationType: BadgeAnimationType.scale,
animationDuration: Duration(seconds: 1),
shape: BadgeShape.circle,
),
Spacer(flex: 4,)
],
),
),
)
);
}
}Here's the resulting application.
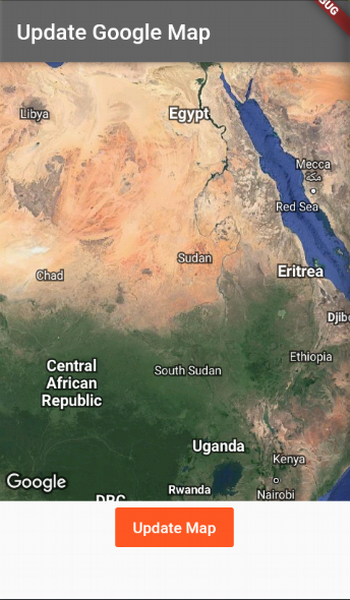
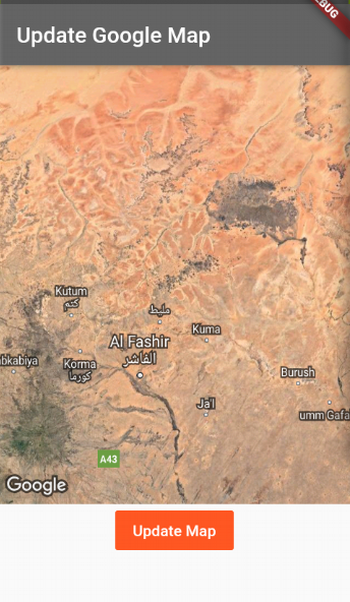
Flutter Google Maps plugin
Adding Google Maps in Flutter apps is a very easy process with the help of the google_maps_flutter plugin.
Note: The Google Maps Flutter plugin is still in developer preview (so it cannot be released to the app store yet). Make sure to wait for the stable release before using it.
The main prerequisites for using this plugin are to have a Google Cloud Platform account and to create a Google Maps API key. If you do not know how to obtain a key, see Google Maps Integration in Flutter.
Once the Google Maps SDK is enabled with a credential/API key, you can use it in your Flutter app. Fill out the following with the key.
For Android:
Go to android>app>src>main>Androidmanifest.xml and make sure that the manifest looks like the following (replacing YOUR KEY HERE with your API key):
<manifest ...
<application ...
<meta-data android:name="com.google.android.geo.API_KEY"
android:value="YOUR KEY HERE"/>For iOS:
Edit the Appdelegate.m file as follows (replacing YOUR KEY HERE with your API key):
@implementation AppDelegate
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions {
[GMSServices provideAPIKey:@"YOUR KEY HERE"];
[GeneratedPluginRegistrant registerWithRegistry:self];
return [super application:application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:launchOptions];
}
@endGoogleMaps widget basics
Now it's time to bring the Maps inside the Flutter application. To begin, add the following dependency in the pubspec.yaml file:
dependencies:
google_maps_flutter: ^0.5.21Import the following package to the main.dart file:
import 'package:google_maps_flutter/google_maps_flutter.dart';This package provides the following widgets:
GoogleMap
The GoogleMap widget provides the main control over Google Maps inside a Flutter application. It has several important attributes that help create the maps you require. They are:
- mapType: This attribute defines what type of map (satellite, hybrid, or normal) is shown. Select one by with the value MapType.satellite, MapType.hybrid, or MapType.normal.
- InitialCameraPosition: The initial camera position is important for rendering the map on the Flutter UI and setting the camera position (from which the camera will move). Set the initial camera position by creating a variable with the CameraPosition class as its value.
- OnMapCreated: This is a callback that fires whenever the camera position changes (e.g., whenever the user moves the map by pinching or swiping it). To move the camera angle programmatically, use GoogleMapController instead.
GoogleMapController
This class controls the Google Map by creating an instance of it. There is no explicit way to change the camera position of the Google Map, but you can use the GoogleMapController to control all sorts of activities on the GoogleMap class.
CameraPosition
The CameraPosition class provides the camera position values that are required to show any position on the GoogleMap.
CameraPosition initPosition = CameraPosition(
target: LatLng(14.5, 25.7), zoom: 7, );The CameraPosition class takes in various attributes, like target, zoom, etc. The Target attribute marks the latitude and longitude position on the Google Map. The class takes in a double value like LatLng(double, double) to mark it at that position.
Example Flutter GoogleMaps app
This example app creates an animated camera transition on a Google Map. This is a very useful way to provide Google Maps in Flutter applications.
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:google_maps_flutter/google_maps_flutter.dart';
void main() => runApp(GoogleMapApp());
class GoogleMapApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Sample GoogleMap Widget',
home: GoogleMapWidget(),
);
}
}
class GoogleMapWidget extends StatefulWidget {
GoogleMapWidget({Key key}) : super(key: key);
@override
_GoogleMapWidgetState createState() => _GoogleMapWidgetState();
}
class _GoogleMapWidgetState extends State {
Completer _controller = Completer();
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
}
CameraPosition initPosition = CameraPosition(
target: LatLng(14.5, 25.7),
zoom: 7,
);
void updateGoogleMap()
async{
GoogleMapController cont = await _controller.future;
setState(() {
CameraPosition newtPosition = CameraPosition(
target: LatLng(14.5, 28.7),
zoom: 4,
);
cont.animateCamera(CameraUpdate.newCameraPosition(newtPosition));
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
backgroundColor: Colors.black45,
title: Text("Update Google Map"),
),
body: Center(
child: Column(
children: [
Container(
height: 400.0,
child: GoogleMap(
mapType: MapType.hybrid,
initialCameraPosition: initPosition,
onMapCreated: (GoogleMapController controller){
_controller.complete(controller);
},
),
),
FlatButton(
child: Text("Update Map", style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),),
color: Colors.deepOrange,
onPressed: (){
updateGoogleMap();
},
)
],
),
));
}
}Here's the resulting application.
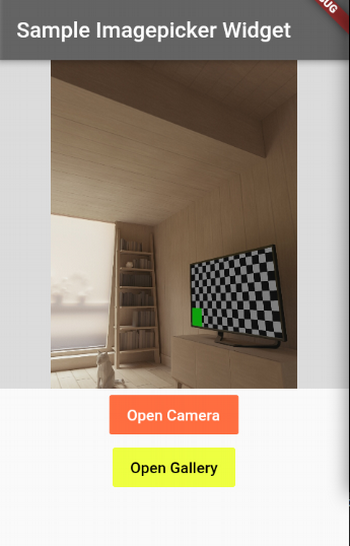
Flutter ImagePicker image gallery plugin
The ImagePicker plugin integrates an image gallery into a Flutter app.
To begin using the image_picker plugin, add the following dependency in the pubspec.yaml file:
dependencies:
image_picker: ^0.6.1+4This requires you to add an import statement in your main file, e.g., main.dart file:
import 'package:image_picker/image_picker.dart';To use the Flutter application in iOS, make the following changes in the info.plist file:
- NSPhotoLibraryUsageDescription: This describes why the app needs permission to use the photo library. This is called Privacy - Photo Library Usage Description in the visual editor.
- NSCameraUsageDescription: This describes why your app needs access to the camera. This is called Privacy - Camera Usage Description in the visual editor.
- NSMicrophoneUsageDescription: This describes why your app needs access to the microphone if you intend to record videos. This is called Privacy - Microphone Usage Description in the visual editor.
Image Picker widget basics
To use the ImagePicker widget, just call the class ImagePicker. There are two options for this class:
- Choose an image or choose a video
- Choose an image or video directly from a gallery or a camera source
This is possible through two method callbacks:
- ImagePicker.pickImage() with the source ImageSource.gallery or ImageSource.camera
- ImagePicker.pickVideo() with the above sources
Both of these calls are async calls, which require setState() on the image or video that is selected.
ImagePicker.<source call> returns the file location of the image/video. You must load the image using the Image.file() call.
All of this is explained in the example application.
Example Flutter ImagePicker widget app
This example app creates an Image Picker button to select an image from the gallery or directly from the camera.
import 'dart:async';
import 'dart:io';
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:image_picker/image_picker.dart';
void main() => runApp(ImagePickerApp());
class ImagePickerApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Sample Imagepicker Widget',
home: ImagePickerWidget(),
);
}
}
class ImagePickerWidget extends StatefulWidget {
ImagePickerWidget({Key key}) : super(key: key);
@override
_ImagePickerWidgetState createState() => _ImagePickerWidgetState();
}
class _ImagePickerWidgetState extends State {
File _image;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
}
void open_camera()
async {
var image = await ImagePicker.pickImage(source: ImageSource.camera);
setState(() {
_image = image;
});
}
void open_gallery()
async {
var image = await ImagePicker.pickImage(source: ImageSource.gallery);
setState(() {
_image = image;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("Sample Imagepicker Widget"),
backgroundColor: Colors.black45,),
body: Center(
child: Container(
child: Column(
children: [
Container(
color: Colors.black12,
height: 300.0,
width: 900.0,
child: _image == null ? Text("Still waiting!") : Image.file(_image),),
FlatButton(
color: Colors.deepOrangeAccent,
child: Text("Open Camera", style: TextStyle(color: Colors.white),),
onPressed: (){
open_camera();
},),
FlatButton(
color: Colors.limeAccent,
child:Text("Open Gallery", style: TextStyle(color: Colors.black),),
onPressed: (){
open_gallery();
},
)
],
),
),
)
);
}
}Here's the resulting application.

Summary
These five plugins are very important for creating a neater UI experience in Flutter apps. They will also help you ramp up faster with Flutter app development.
Some of the information in this article was previously published at Android Monks.










1 Comment