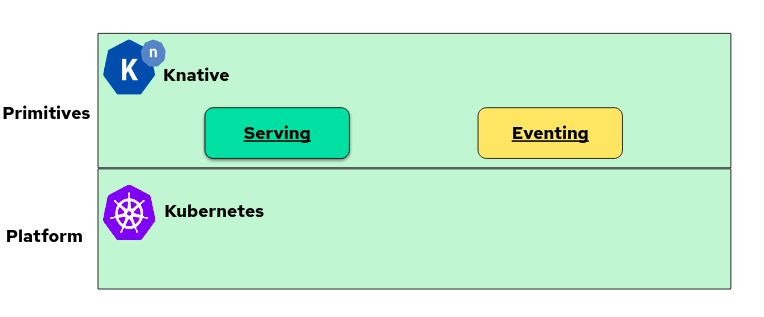
Knative is an open source project based on the Kubernetes platform for building, deploying, and managing serverless workloads that run in the cloud, on-premises, or in a third-party data center. Google originally started it with contributions from more than 50 companies.
Knative allows you to build modern applications which are container-based and source-code-oriented.
Knative Core Projects
Knative consists of two components: Serving and Eventing. It's helpful to understand how these interact before attempting to develop Knative applications.
(Savita Ashture, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Knative Serving
Knative Serving is responsible for features revolving around deployment and the scaling of applications you plan to deploy. This also includes network topology to provide access to an application under a given hostname.
Knative Serving focuses on:
- Rapid deployment of serverless containers.
- Autoscaling includes scaling pods down to zero.
- Support for multiple networking layers such as Ambassador, Contour, Kourier, Gloo, and Istio for integration into existing environments.
- Give point-in-time snapshots of deployed code and configurations.
Knative Eventing
Knative Eventing covers the event-driven nature of serverless applications. An event-driven architecture is based on the concept of decoupled relationships between event producers that create events and event consumers, or sinks, that receive events.
Knative Eventing uses standard HTTP POST requests to send and receive events between event producers and sinks.
In this article, I focus on the Serving project since it is the most central project of Knative and helps deploy applications.
The Serving project
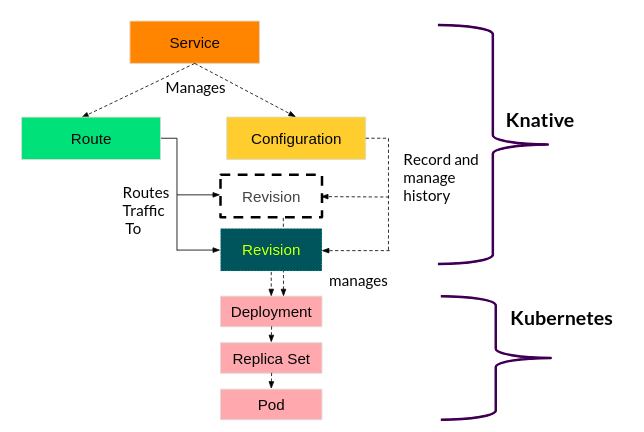
Knative Serving defines a set of objects as Kubernetes Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs). These objects get used to define and control how your serverless workload behaves on the cluster:
(Savita Ashture, CC BY-SA 4.0)
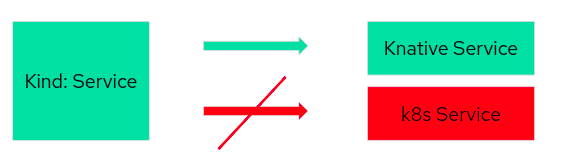
- Service: A Knative Service describes a combination of a route and a configuration as shown above. It is a higher-level entity that does not provide any additional functionality. It should make it easier to deploy an application quickly and make it available. You can define the service to always route traffic to the latest revision or a pinned revision.
(Savita Ashture, CC BY-SA 4.0)
- Route: The Route describes how a particular application gets called and how the traffic gets distributed across the different revisions. There is a high chance that several revisions can be active in the system at any given time based on the use case in those scenarios. It's the responsibility of routes to split the traffic and assign to revisions.
- Configuration: The Configuration describes what the corresponding deployment of the application should look like. It provides a clean separation between code and configuration and follows the Twelve-Factor App methodology. Modifying a configuration creates a new revision.
- Revision: The Revision represents the state of a configuration at a specific point in time. A revision, therefore, gets created from the configuration. Revisions are immutable objects, and you can retain them for as long as useful. Several revisions per configuration may be active at any given time, and you can automatically scale up and down according to incoming traffic.
Deploying an application using Knative Service
To write an example Knative Service, you must have a Kubernetes cluster running. If you don't have a cluster, you can run a local single-node cluster with Minikube. Your cluster must have at least two CPUs and 4GB RAM available.
You must also install Knative Serving and its required dependencies, including a networking layer with configured DNS.
Follow the official installation instructions before continuing.
Here's a simple YAML file (I call it article.yaml) that deploys a Knative Service:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: knservice
namespace: default
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- image: docker.io/##DOCKERHUB_NAME##/demoWhere ##DOCKERHUB_NAME## is a username for dockerhub.
For example, docker.io/savita/demo.
This is a minimalist YAML definition for creating a Knative application.
Users and developers can tweak YAML files by adding more attributes based on their unique requirements.
$ kubectl apply -f article.yaml
service.serving.knative.dev/knservice createdThat's it! You can now observe the different resources available by using kubectl as you would for any other Kubernetes process.
Take a look at the service:
$ kubectl get ksvc
NAME URL LATESTCREATED LATESTREADY READY REASON
knservice https://knservice.default.example.com knservice-00001 knservice-00001 True
You can view the configuration:
$ kubectl get configurations
NAME LATESTCREATED LATESTREADY READY REASON
knservice knservice-00001 knservice-00001 TrueYou can also see the routes:
$ kubectl get routes
NAME URL READY REASON
knservice https://knservice.default.example.com TrueYou can view the revision:
$ kubectl get revision
NAME CONFIG NAME K8S SERVICE NAME GENERATION READY REASON ACTUAL REPLICAS DESIRED REPLICAS
knservice-00001 knservice 1 True 1 1You can see the pods that got created:
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
knservice-00001-deployment-57f695cdc6-pbtvj 2/2 Running 0 2m1sScaling to zero
One of the properties of Knative is to scale down pods to zero if no request gets made to the application. This happens if the application does not receive any more requests for five minutes.
$ kubectl get pods
No resources found in default namespace.The application becomes scaled to zero instances and no longer needs any resources. And this is one of the core principles of Serverless: If no resources are required, then none are consumed.
Scaling up from zero
As soon as the application is used again (meaning that a request comes to the application), it immediately scales to an appropriate number of pods. You can see that by using the curl command:
$ curl https://knservice.default.example.com
Hello Knative!Since scaling needs to occur first, and you must create at least one pod, the requests usually last a bit longer in most cases. Once it successfully finishes, the pod list looks just like it did before:
$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
knservice-00001-deployment-57f695cdc6-5s55q 2/2 Running 0 3sConclusion
Knative has all those best practices which a serverless framework requires. For developers who already use Kubernetes, Knative is an extension solution that is easily accessible and understandable.
In this article, I've shown how Knative Serving works in detail, how it achieves the quick scaling it needs, and how it implements the features of serverless.









Comments are closed.