Sometimes it's useful to get visual feedback from a script. For example, when a script or cron job completes, a long-running build fails, or there is an urgent problem during script execution. Desktop applications can do this with popup notifications, but it can be done from a script too! You can use script commands to send yourself desktop notifications and reminders.
(Tomasz Waraksa, CC BY-SA 4.0)
The below code has been written and tested on Linux. It can also be done on macOS with a bit of effort. See the last section for some hints and tips.
Sending notifications from the Linux terminal
To send notifications from the Linux terminal, use the notify-send command. It's often already installed as a part of your desktop, but you can run which notify-send to confirm. If it's not installed yet, install it with your package manager of choice.
On Fedora and similar distributions, type:
$ sudo dnf install libnotify
On Debian-based distributions, type:
$ sudo apt install notify-sendA few examples of simple notifications:
$ notify-send "Dinner ready!"
$ notify-send "Tip of the Day" "How about a nap?"You can customize the notification with options such as urgency level, custom icon, and so on. Find out more with man notify-send. You can use a small set of HTML tags in the notification body to give your messages a nice touch. On top of that, URLs are rendered as clickable. For example:
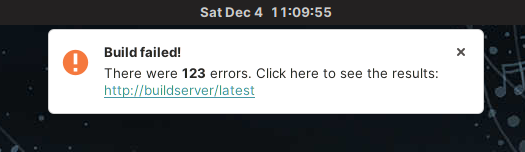
$ notify-send -u critical \
"Build failed!" \
"There were <b>123</b> errors. Click here to see the results: http://buildserver/latest"
(Tomasz Waraksa, CC BY-SA 4.0)
Sent notifications are picked up by the desktop environment and displayed just like any other notification. They will have the same consistent look, feel, and behavior.
Combine notify-send with at
Cron is commonly used to schedule commands at regular intervals. The at command schedules the single execution of a command at a specified time. If you run it like this, it starts in interactive mode, where you can enter commands to execute at a given time:
$ at 12:00This isn't useful for scripts. Luckily, at accepts parameters from standard input so that we can use it this way:
$ echo "npm run build" | at now + 1 minute
$ echo "backup-db" | at 13:00There are many ways of specifying time. From absolute time, such as 10:00 through relative time, such as now + 2 hours, to special times such as noon or midnight. We can combine it with notify-send to show ourselves reminders at some time in the future. For example:
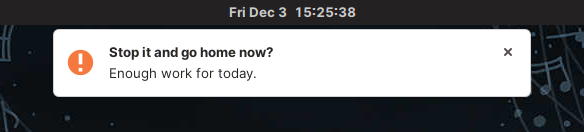
$ echo "notify-send 'Stop it and go home now?' 'Enough work for today.' -u critical" | at now
(Tomasz Waraksa, CC BY-SA 4.0)
The remind command
Now, build a custom Bash command for sending yourself reminders. How about something as simple and human-friendly as:
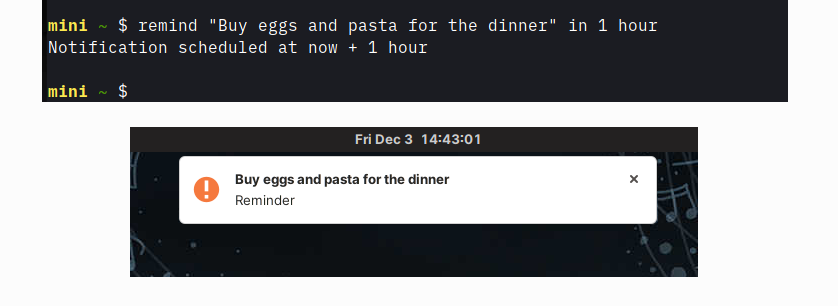
$ remind "I'm still here" now
$ remind "Time to wake up!" in 5 minutes
$ remind "Dinner" in 1 hour
$ remind "Take a break" at noon
$ remind "It's Friday pints time!" at 17:00
This is better than Alexa! How to get this goodness?
See the code below. It defines a shell function called remind, which supports the above syntax. The actual work is done in the last two lines. The rest is responsible for help, parameter validation, etc., which roughly matches the proportion of useful code vs. necessary white-noise in any large application.
Save the code somewhere, for example, in the ~/bin/remind file, and source the function in your .bashrc profile so that it's loaded when you log in:
$ source ~/bin/remindReload the terminal, then type remind to see the syntax. Enjoy!
#!/usr/bin/env bash
function remind () {
local COUNT="$#"
local COMMAND="$1"
local MESSAGE="$1"
local OP="$2"
shift 2
local WHEN="$@"
# Display help if no parameters or help command
if [[ $COUNT -eq 0 || "$COMMAND" == "help" || "$COMMAND" == "--help" || "$COMMAND" == "-h" ]]; then
echo "COMMAND"
echo " remind <message> <time>"
echo " remind <command>"
echo
echo "DESCRIPTION"
echo " Displays notification at specified time"
echo
echo "EXAMPLES"
echo ' remind "Hi there" now'
echo ' remind "Time to wake up" in 5 minutes'
echo ' remind "Dinner" in 1 hour'
echo ' remind "Take a break" at noon'
echo ' remind "Are you ready?" at 13:00'
echo ' remind list'
echo ' remind clear'
echo ' remind help'
echo
return
fi
# Check presence of AT command
if ! which at >/dev/null; then
echo "remind: AT utility is required but not installed on your system. Install it with your package manager of choice, for example 'sudo apt install at'."
return
fi
# Run commands: list, clear
if [[ $COUNT -eq 1 ]]; then
if [[ "$COMMAND" == "list" ]]; then
at -l
elif [[ "$COMMAND" == "clear" ]]; then
at -r $(atq | cut -f1)
else
echo "remind: unknown command $COMMAND. Type 'remind' without any parameters to see syntax."
fi
return
fi
# Determine time of notification
if [[ "$OP" == "in" ]]; then
local TIME="now + $WHEN"
elif [[ "$OP" == "at" ]]; then
local TIME="$WHEN"
elif [[ "$OP" == "now" ]]; then
local TIME="now"
else
echo "remind: invalid time operator $OP"
return
fi
# Schedule the notification
echo "notify-send '$MESSAGE' 'Reminder' -u critical" | at $TIME 2>/dev/null
echo "Notification scheduled at $TIME"
}Easy notifications
With these few simple open source commands, you can integrate your own scripts, applications, and tasks with your desktop. Try it out!
This article has been adapted with the author's permission from the original article, found here.






5 Comments