FreeDOS is an old operating system, but it is new to many people. In 1994, several developers and I came together to create FreeDOS—a complete, free, DOS-compatible operating system you can use to play classic DOS games, run legacy business software, or develop embedded systems. Any program that works on MS-DOS should also run on FreeDOS.
In 1994, FreeDOS was immediately familiar to anyone who had used Microsoft's proprietary MS-DOS. And that was by design; FreeDOS intended to mimic MS-DOS as much as possible. As a result, DOS users in the 1990s were able to jump right into FreeDOS. But times have changed. Today, open source developers are more familiar with the Linux command line or they may prefer a graphical desktop like GNOME, making the FreeDOS command line seem alien at first.
New users often ask, "I installed FreeDOS, but how do I use it?" If you haven't used DOS before, the blinking C:\> DOS prompt can seem a little unfriendly. And maybe scary. This gentle introduction to FreeDOS should get you started. It offers just the basics: how to get around and how to look at files. If you want to learn more than what's offered here, visit the FreeDOS wiki.
The DOS prompt
First, let's look at the empty prompt and what it means.
opensource.com
DOS is a "disk operating system" created when personal computers ran from floppy disks. Even when computers supported hard drives, it was common in the 1980s and 1990s to switch frequently between the different drives. For example, you might make a backup copy of your most important files to a floppy disk.
DOS referenced each drive by a letter. Early PCs could have only two floppy drives, which were assigned as the A: and B: drives. The first partition on the first hard drive was the C: drive, and so on for other drives. The C: in the prompt means you are using the first partition on the first hard drive.
Starting with PC-DOS 2.0 in 1983, DOS also supported directories and subdirectories, much like the directories and subdirectories on Linux filesystems. But unlike Linux, DOS directory names are delimited by \ instead of /. Putting that together with the drive letter, the C:\ in the prompt means you are in the top, or "root," directory of the C: drive.
The > is the literal prompt where you type your DOS commands, like the $ prompt on many Linux shells. The part before the > tells you the current working directory, and you type commands at the > prompt.
Finding your way around in DOS
The basics of navigating through directories in DOS are very similar to the steps you'd use on the Linux command line. You need to remember only a few commands.
Displaying a directory
When you want to see the contents of the current directory, use the DIR command. Since DOS commands are not case-sensitive, you could also type dir. By default, DOS displays the details of every file and subdirectory, including the name, extension, size, and last modified date and time.
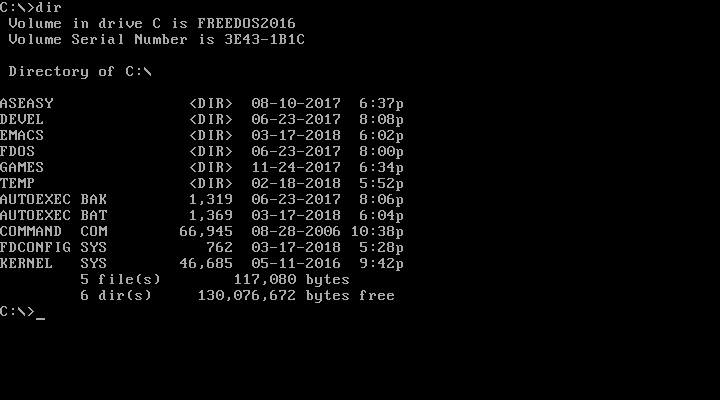
opensource.com
If you don't want the extra details about individual file sizes, you can display a "wide" directory by using the /w option with the DIR command. Note that Linux uses the hyphen (-) or double-hyphen (--) to start command-line options, but DOS uses the slash character (/).
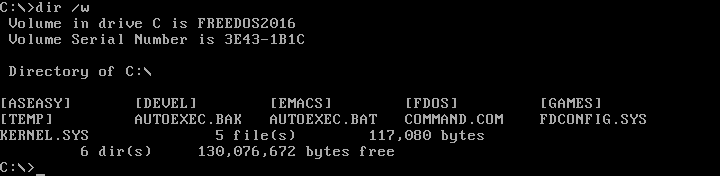
opensource.com
You can look inside a specific subdirectory by passing the pathname as a parameter to DIR. Again, another difference from Linux is that Linux files and directories are case-sensitive, but DOS names are case-insensitive. DOS will usually display files and directories in all uppercase, but you can equally reference them in lowercase.
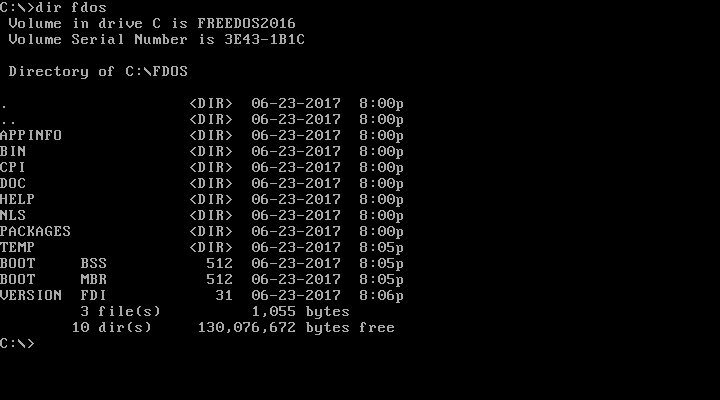
opensource.com
Changing the working directory
Once you can see the contents of a directory, you can "move into" any other directory. On DOS, you change your working directory with the CHDIR command, also abbreviated as CD. You can change into a subdirectory with a command like CD CHOICE or into a new path with CD \FDOS\DOC\CHOICE.
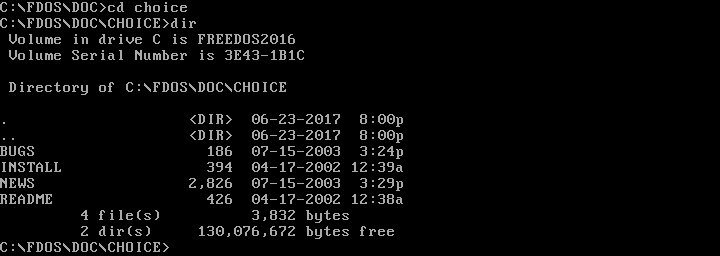
opensource.com
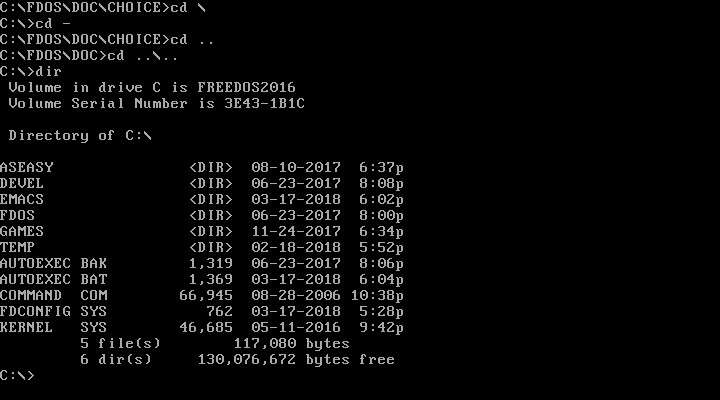
Just like on the Linux command line, DOS uses . to represent the current directory, and .. for the parent directory (one level "up" from the current directory). You can combine these. For example, CD .. changes to the parent directory, and CD ..\.. moves you two levels "up" from the current directory.
FreeDOS also borrows a feature from Linux: You can use CD - to jump back to your previous working directory. That is handy after you change into a new path to do one thing and want to go back to your previous work.
opensource.com
Changing the working drive
Under Linux, the concept of a "drive" is hidden. In Linux and other Unix systems, you "mount" a drive to a directory path, such as /backup, or the system does it for you automatically, such as /var/run/media/user/flashdrive. But DOS is a much simpler system. With DOS, you must change the working drive by yourself.
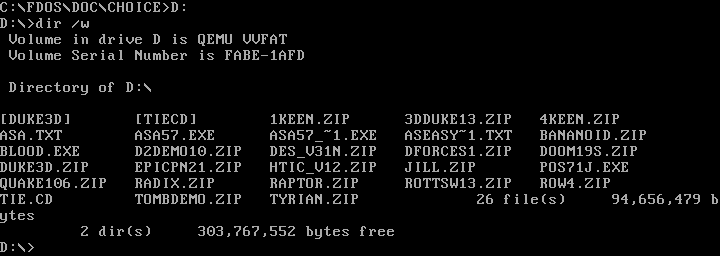
Remember that DOS assigns the first partition on the first hard drive as the C: drive, and so on for other drive letters. On modern systems, people rarely divide a hard drive with multiple DOS partitions; they simply use the whole disk—or as much of it as they can assign to DOS. Today, C: is usually the first hard drive, and D: is usually another hard drive or the CD-ROM drive. Other network drives can be mapped to other letters, such as E: or Z: or however you want to organize them.
Changing drives is easy under DOS. Just type the drive letter followed by a colon (:) on the command line, and DOS will change to that working drive. For example, on my QEMU system, I set my D: drive to a shared directory in my Linux home directory, where I keep installers for various DOS applications and games I want to test.
opensource.com
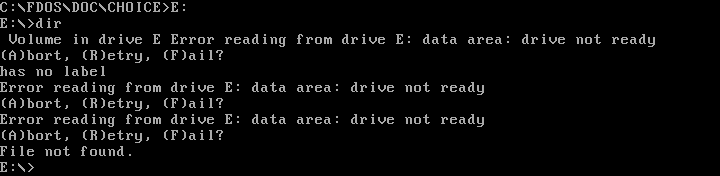
Be careful that you don't try to change to a drive that doesn't exist. DOS may set the working drive, but if you try to do anything there you'll get the somewhat infamous "Abort, Retry, Fail" DOS error message.
opensource.com
Other things to try
With the CD and DIR commands, you have the basics of DOS navigation. These commands allow you to find your way around DOS directories and see what other subdirectories and files exist. Once you are comfortable with basic navigation, you might also try these other basic DOS commands:
MKDIRorMDto create new directoriesRMDIRorRDto remove directoriesTREEto view a list of directories and subdirectories in a tree-like formatTYPEandMOREto display file contentsRENAMEorRENto rename filesDELorERASEto delete filesEDITto edit filesCLSto clear the screen
If those aren't enough, you can find a list of all DOS commands on the FreeDOS wiki.
In FreeDOS, you can use the /? parameter to get brief instructions to use each command. For example, EDIT /? will show you the usage and options for the editor. Or you can type HELP to use an interactive help system.
Like any DOS, FreeDOS is meant to be a simple operating system. The DOS filesystem is pretty simple to navigate with only a few basic commands. So fire up a QEMU session, install FreeDOS, and experiment with the DOS command line. Maybe now it won't seem so scary.







Comments are closed.