Configuring a network connection from a Linux machine can be challenging. Fortunately, many new Linux distributions come with some type of network management tool that can help you automatically connect to a wireless network. But wouldn't it be nice to be able to set up a static network connection from a Linux machine? This guide will show you how to use different Linux tools to check for network connections from a CentOS/RHEL machine and explain how to add a static network using the nmcli tool.
Step 1: Check network connectivity
The ping command is a well-known utility that quickly checks for a connection to an address. Enter the following on the command line:
ping -c3 opensource.comwhere the -c3 parameter option indicates you will call this domain name only three times.
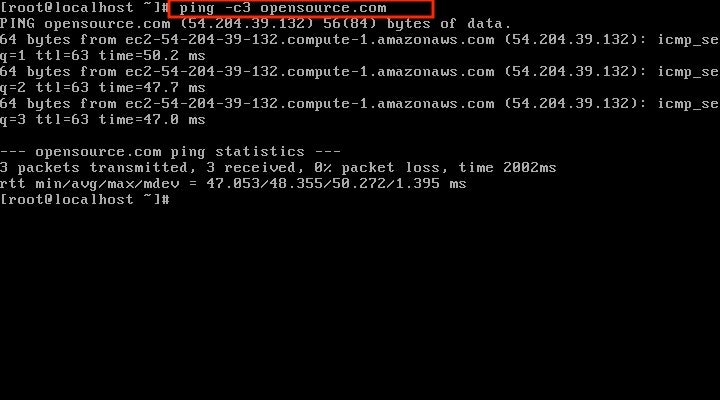
If you are connected to the internet, you will get a data packet response like the one at the bottom of this screenshot.
Step 2: Check connection information
You can check network information using the ip add command.
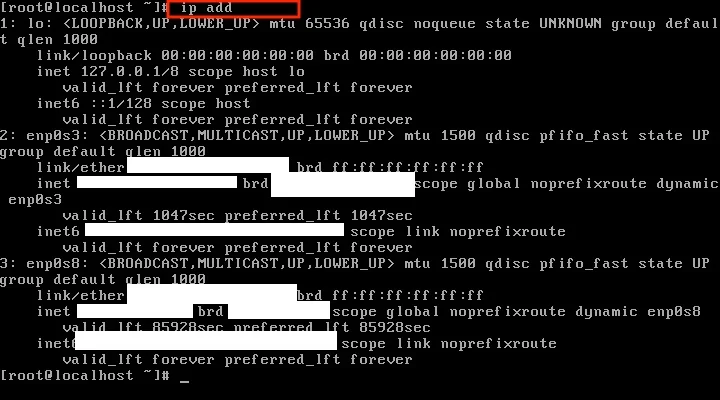
Running this command shows device information, the IP address, and more. You'll need some of this information, like the device info and IP address, later to set up a static connection, so go ahead and grab it.
Step 3: Check network information
Network information can be found inside the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts directory by entering:
ls /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts
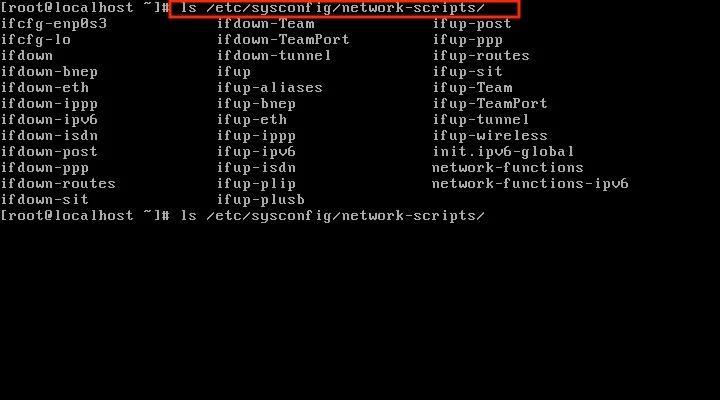
For example, this screenshot shows ifcfg-enp0s3 and ifcfg-lo, but this will vary depending on where you are running Linux and how your device is set up.
Step 4: Show available connections
The nmcli tool shows the available connections currently used to connect to the network. Enter the following command:
nmcli con show
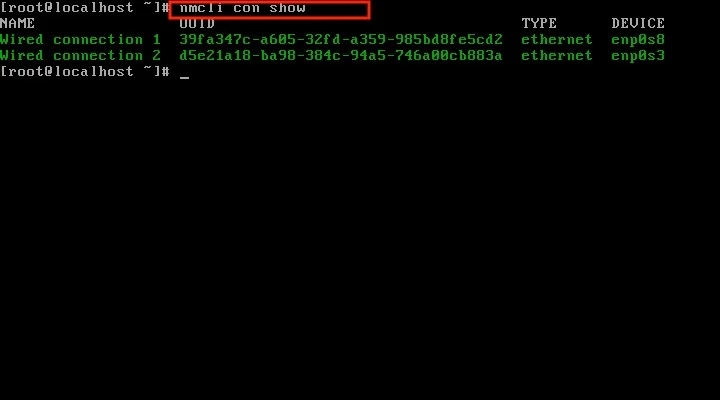
This screenshot shows two devices are active: enp0s8 and enp0s3, and they are called Wired Connection 1 and 2. But this can be different, depending on how your Linux environment is set up.
Step 5: Check that the network connection is on
You used the ping command above to check that you can receive data packets, but now use the systemctl command for network to monitor, update, and troubleshoot the network. The command is:
systemctl status network
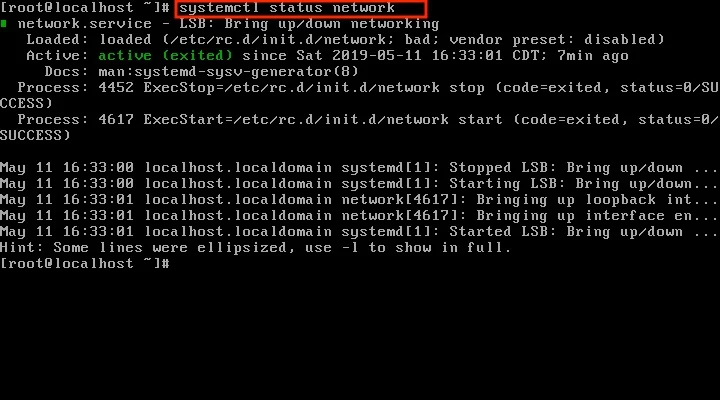
If the network utility has no issues, you will see the status as active when you run this command.
Step 6: Add the static connection
Now you're ready to add a static connection. Using the device name you grabbed from ip add in Step 2, modify and enter the following command to add a new connection:
nmcli con add con-name "SomeName" ifname YOUR_DEVICE autoconnect yes type YOUR_CONNECTION_TYPEChange SomeName, YOUR_DEVICE, and YOUR_CONNECTION_TYPE based on your configuration.
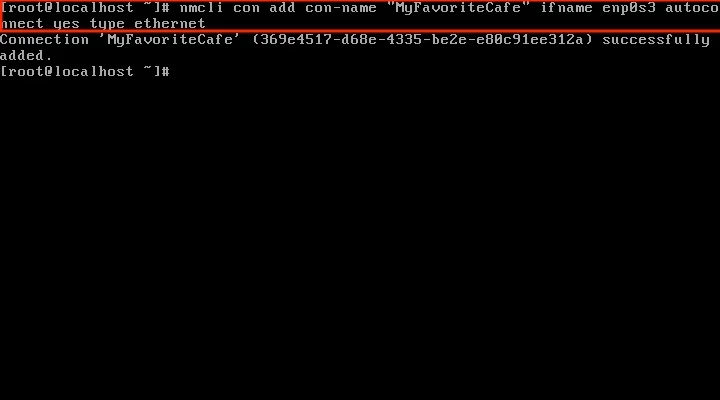
Step 7: Verify the connection is added to the network-scripts path
There are two ways to modify the new connection info using the nmcli tool. One is by using the following command:
nmcli con modThis command essentially modifies the network configuration scripts under the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts directory, which is the other way to modify connection information. Choose the option to modify the connection directly.
Look into the /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts path again by entering:
ls /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts
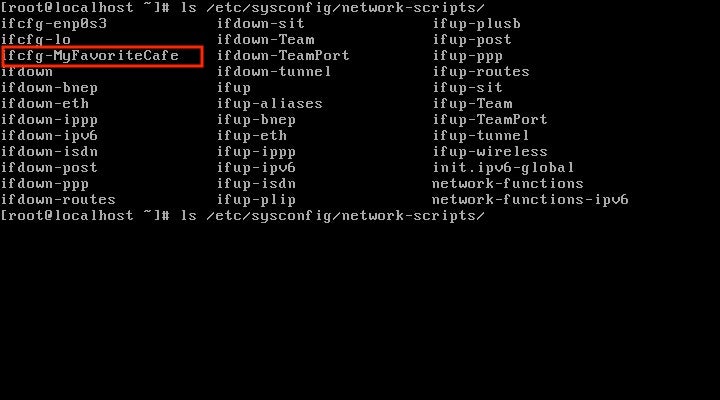
You can see that the connection ifcfg-MyFavoriteCafe was added.
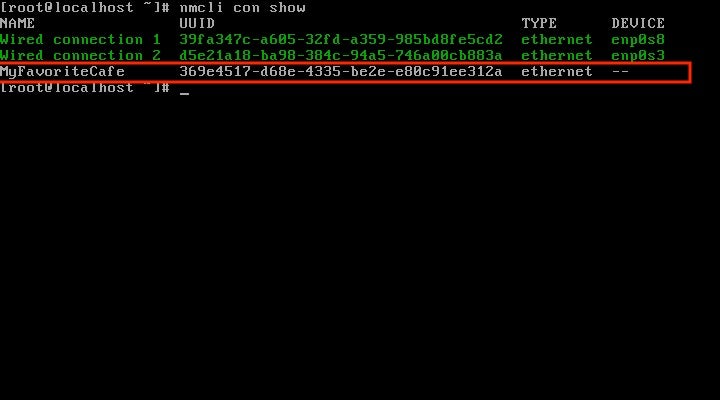
Step 8: Confirm you can see the connection
Check that MyFavoriteCafe is visible as the available connection. Use the following command to bring the connection up. Please note that SOME_CONNECTION_NAME is the name of your connection (it is MyFavoriteCafe in this example).
nmcli con up SOME_CONNECTION NAMEor bring it down using the following command:
nmcli con down SOME_CONNECTION NAMEWhen you added the new connection, autoconnect was set to be true, so it will automatically start if you restart the network utility.
So far, so good. The connection shows up when you run the following command:
Step 9: Modify the connection to be static
Open the file /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-SOME_CONNECTION_NAME (it is MyFavoriteCafe in this example), using a text editor, such as Vim, Emacs, or Nano. (If you want a quick introduction to Vi or Vim, check out my intro guide, "Getting started with Vim: The basics.")
To make the connection static, modify one parameter and add three parameters:
- Modify BOOTPROTO to be static.
- Add IPADDR. This can be found from the ip add command or your connected network.
- Add NETMASK. This can be found from the ip add command or your connected network.
- Add GATEWAY. This can be found from the ip add command or your connected network.
You might also need to add DNS, PREFIX, or other information, depending on how your network and the machine are set up.
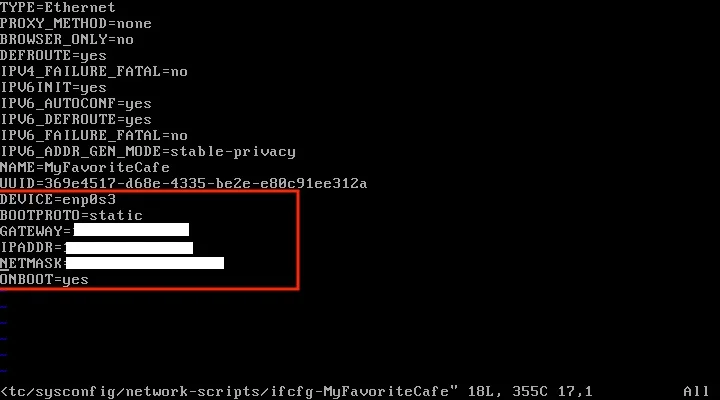
Once you've done this, save the file. Restart the network with the following command:
systemctl restart networkCheck the status with:
systemctl status networkStep 10: Confirm the new connection is active
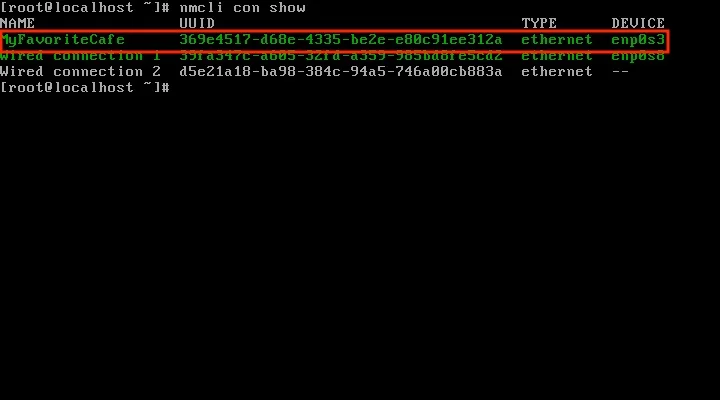
That should do it! But make sure by checking if the new connection is working. Run the nmcli con show command again to start the new connection.
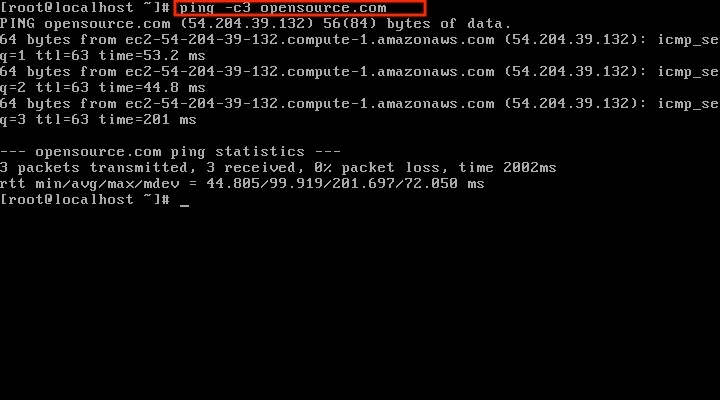
You can also ping a website address to verify that the connection is working.
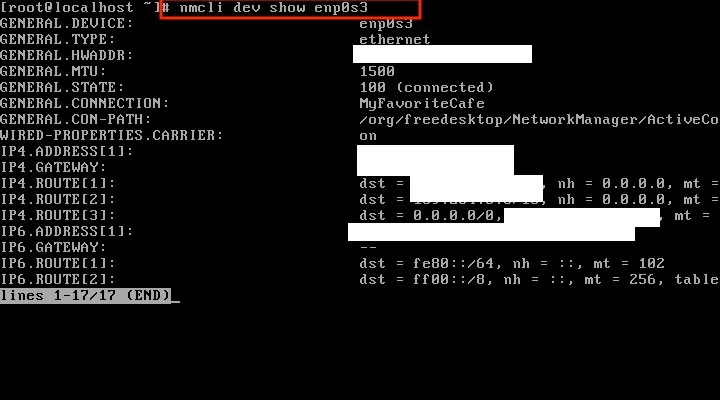
Finally, you can check the device info using the following command:
nmcli dev show DEVICE_NAMEwhere DEVICE_NAME is the name of your network device.
If you have any questions or feedback, please leave them in the comments.







8 Comments